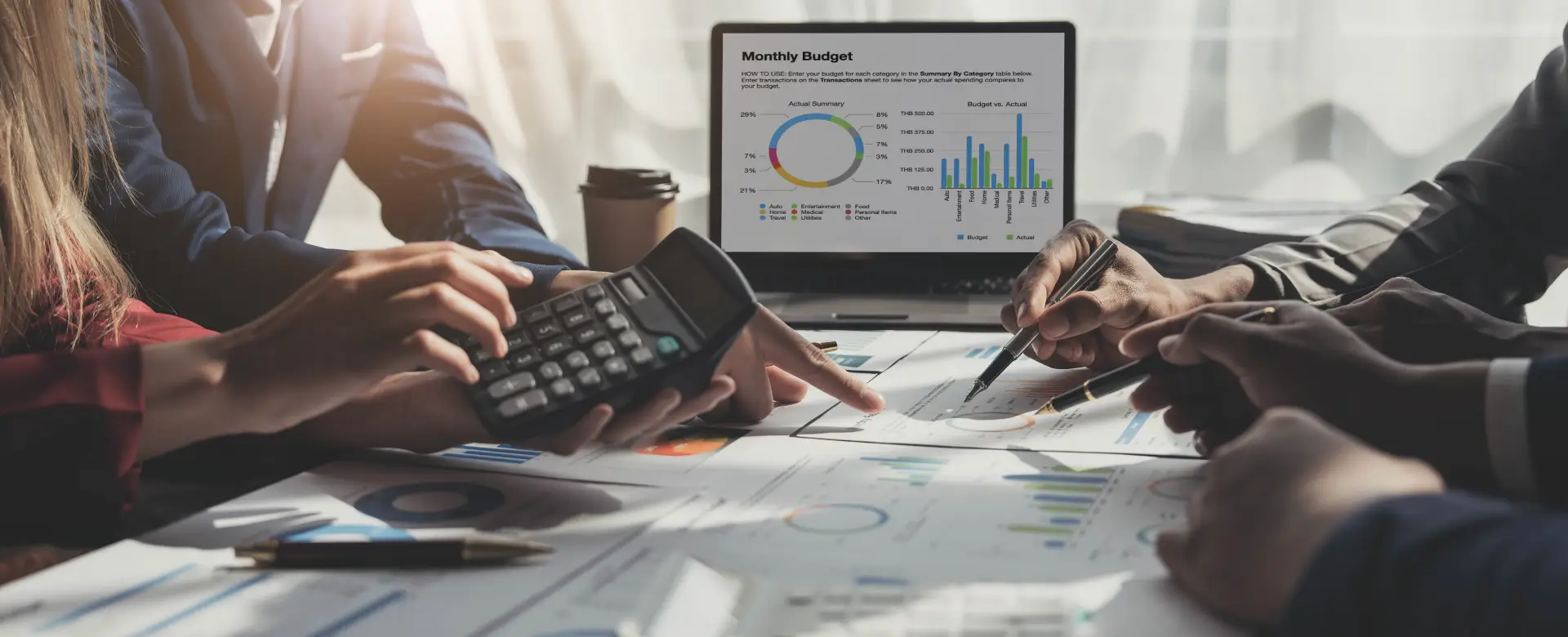
The financial sector is undergoing a significant transformation, with the global fintech market projected to reach $324 billion by 2026. Innovations in digital banking, mobile payments, blockchain, and AI are driving this growth. Customers demand instant access, personalized services, and seamless experiences. However, this rapid digital evolution has heightened cybersecurity risks, with average data breach costs in the sector reaching $6.08 million in 2024.
Background
In 2016, Bangladesh Bank, the country’s central bank, suffered a sophisticated cyber heist. Attackers exploited vulnerabilities to initiate unauthorized transfers through the SWIFT network, a global platform for international money transfers.

Attack
- Method: Attackers gained access via phishing emails, installed malware, and stole credentials for SWIFT terminals.
- On February 4, 2016, the attackers attempted to transfer $1 billion from Bangladesh Bank’s account at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
- A spelling error flagged some transactions, but $101 million was successfully transferred, with $81 million laundered through Philippine casinos.
Impact
- Financial Loss: Bangladesh Bank lost $81 million, a significant sum for a developing nation.
- Reputation: Confidence in the bank and broader financial systems was shaken.
- Systemic Risk: Concerns arose about the security of the SWIFT network, used globally by financial institutions.